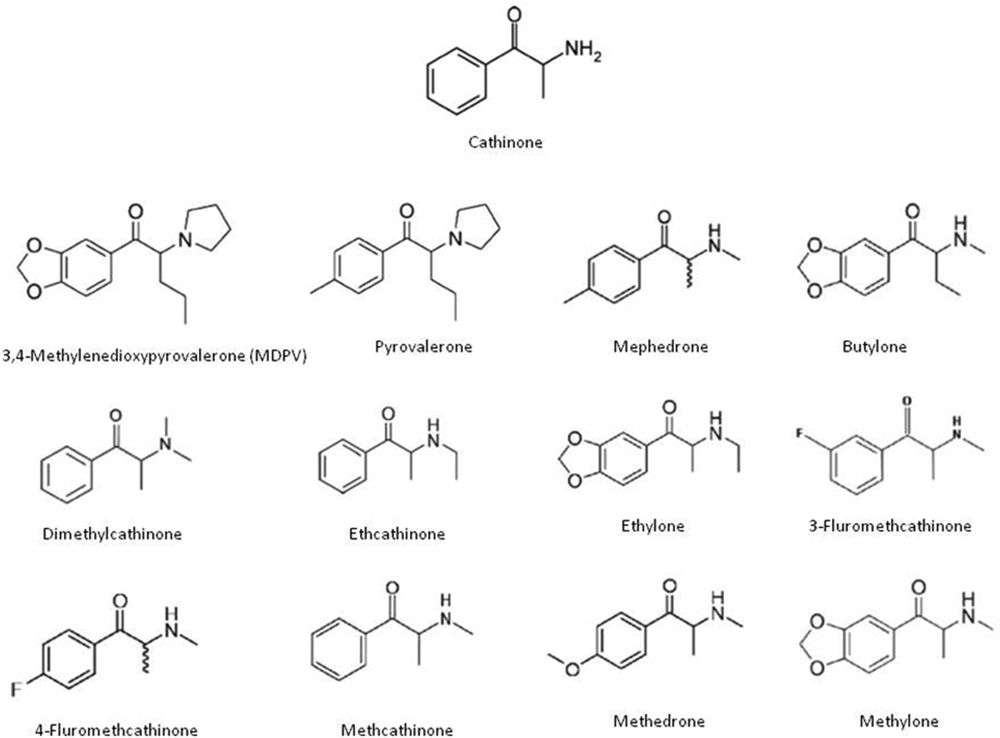
Synthetic cathinones
Synthetic cathinones are a subgroup of NSAIDs that can be considered as structural derivatives of cathinone, which is the main active ingredient of the cat plant.
Thus, synthetic cathinones are β–ketophenethylamines, and methcathinone, for example, is also known as β-ketoamphetamine and has a stimulating effect similar to that of amphetamine. A number of synthetic cathinones are under international control. These include cathinone, methcathinone, cathine and pyrovaleron, which came under international control before 2000. However, in the following years, a number of uncontrolled synthetic cathinones appeared on the drug markets, and methylene became the first synthetic cathinone reported to the European Monitoring Center for Drugs and Drug Addiction (ECMN) in 2005. Mephedrone, which was first reported in 2007, became the most widely used cathinone in subsequent years (although it was first synthesized in 1928).
Synthetic cathinones, as a rule, are a white or whitish powder, although there may be other colors. For example, mephedrone is usually a white or yellow powder or crystals with a characteristic odor, described as resembling the smell of fish, vanilla or bleach (bleach). Although mephedrone is found mainly in powder form, it is sometimes also produced in the form of various capsules or tablets.
Consumption and abuse
Synthetic cathinones are usually taken by insufflation (nasal inhalation) or orally. In recent years, the use of synthetic cathinones by injection has also been reported. Doses for nasal administration usually range from 20 to 80 mg, although they can be either lower, for example 5 mg, or higher in some cases – up to 125 mg, with the maximum effect achieved in less than 30 minutes. According to reports, the maximum effect of mephedrone, which requires a high dose for insufflation, occurs 45 minutes to 2 hours after administration and lasts 2-3 hours.
Pharmacology and Toxicology
Some synthetic cathinones are structurally similar to amphetamine–type stimulants – amphetamine, methamphetamine and MDMA and, according to available data, have similar stimulating effects on the central nervous system (CNS). They can have a pronounced effect on the level and nature of the action of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine.
Synthetic cathinones cause a variety of behavioral reactions and can affect motor activity, thermoregulation, learning and memory. Short-term adverse effects observed after the use of mephedrone are diverse and may include loss of appetite, blurred vision, anxiety, depression after the use of the drug, confusion, hallucinations, short-term psychosis and mania. Similarly, clinical reports indicate that the use of MDPV can cause anxiety, paranoia, memory loss and aggression. Intoxication with synthetic cathinones can also lead to severe consequences such as acute liver failure, acute renal failure, high blood pressure and tremor. A number of users of synthetic cathinones reported that with prolonged use they developed tolerance, dependence and withdrawal syndrome.
